|

Subscribe to the project newsletter:
Each of the units below indicates a particular learner level (A1-C2). A summary of the unit’s content is provided, along with a description of how the unit addresses the 5 main areas of CLIL (Content, Communication, Cognition, Competences, and Community). Learn more about CLIL: https://www.languages.dk/clil4u/index.html
Christmas traditions in Denmark
Learner level
A2-B1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
A Danish family celebrates yule (Christmas). We follow the preparations for the yuletide and meet Danish traditions and links to history. The home has been decorated for Christmas with "nisser" (pixies or gnomes), the family decorates the Christmas tree on December 23rd, we also meet the family on Christmas Eve, which is the main Christmas event in Denmark. After the Christmas Eve the family and friends celebrate Christmas with lunches on the first two days of Christmas.
The Clilstore unit has links to linguistic tasks (crosswords, mixed sentences and find the right half of a sentence)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
How Christmas is celebrated in a typical Danish family with presentations of the traditions that have roots starting from the Norse gods up to present times with the Christmas lunch.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
Students will learn vocabulary dealing with the Christmas season; e.g. nisser, julekalender, kravlenisser, and solhverv
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
Students will be using various cognitive skills and will develop both HOTS and LOTS. The students will be able to compare the seasonal tradions from around year 1000 to present days traditions, e.g. bringing in tree branches to celebrate the turning of the sun wheel and to celebrate Odin (number one Norse god)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The unit is mainly made for reading and listening competences, the content will give the students a historical understanding of the Christmas tradititions, thus bringing in history and culture with CLIL scaffolding suitable for different learning situations
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
.From the beginning of November the supermarkeds start displaying Christmas decorations and already in the last week of November every city accross Denmark lits its Christmas tree. Many Danes may not really understand the traditions involved in the celebrations so the unit targets both the Danish population as well as the immigrants. In Denmark some of the Christmas traditions have been taken up by people from other religious communities (especially the gifts and some decorations)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8112
Statsministerens nytårstale 1. januar 2020
Learner level
B1-B2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In Denmark, there is a tradition that the Prime Minister will hold a New Year's speech on 1 January. This unit uses the Prime Minister's speech from 2020. After the transscribed speech, there is a small linguistic exercise (a fill-in the blanks exercise made with https://learningapps.org/).
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Video and text from the Prime Minister's New Year's speech. After the text, there is a little fill-in the blanks exercise and suggestions for group work on the content
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The first part of the task is to decode (listen and understand) the prime minister's speech, this can be followed by group work in which the participants present the main topics that the prime minister has chosen to include in her speech. It is also possible in groups to debate which topics that were not included in the speech - and why.
In conclusion, each group can prepare an alternative New Year speech that will be presented to the class.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after the work of decoding the speech proposes an analysis of the speech content which involves both lower and higher order thinking LOTS and HOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
1. Understanding the speech content and being able to reproduce it (LOTS)
2. Being able to decode the messages and relate critically to the content (HOTS)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Participants are able to decode political messages in a New Year's speech and to be able to relate critically to the topics of the speech.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
.In Denmark, it is a tradition for the Prime Minister to hold a New Year's speech in connection with the New Year, which is transmitted on radio and television.
It was Prime Minister Thorvald Stauning who held the very first New Year's speech in 1940. However, it was not until 1946 that it became a permanent task for the Prime Minister to hold New Year's speech.
Until 1959, the speeches were broadcast exclusively on the radio. From 1961 (in 1960 there was no New Year's speech due to illness) the speakers were broadcast both on radio and television.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8108
Guidance for risk assessment for electrical work on live switchboards
Learner level
B2-C1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
This unit is based on a video "Guidance for risk assessment of electricity work on live switchboards", prepared by the Danish Safety Agency and TEKNIQ in collaboration with the Danish Electricity Association. The video shows considerations to be done before working on a live switchboard.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
This unit is prepared for use in technical schools or for individual safety training. The assignment shows some important assessments that must be taken before working on live electrical panels. After working with video and text, there are optional tasks and tests from the Safety4El project.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The first part of the assignment is to decode (listen and understand) safety aspects in the work with live electrical switchboards, this can be followed by a small task doing learning apps and a group work presentation where the results are presented to the whole class.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after decoding the content in text and video proposes an analysis of the risks of work with live installations, which involves both lower and higher order thinking LOTS and HOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
1. Understanding the content of the text and reproducing it (LOTS)
2. Being able to transfer the situation under review to personal experience and to realize the need for a thorough risk assessment before commencing work (HOTS)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Participants gain skills in making safety assessments at work with live installations. Linguistic competences are strengthened with subject related vocabulary and conversations about safety.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
It is mandatory for electricians to receive guidance and instruction on safety when working with live installations. In Denmark, until 2018-2019 there has been a law stipolating this "L-AUS" which has now been replaced by international regulations, to ensure that an electrician has the necessary skills and is instructed when new work situations occur.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8199
Montering af et stik (Wiring a plug)
Learner level
A1-A2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
This unit ,akes use of an older video showing how to wire a British plug. The British plug looks different from a Danish one, but the process is the same. Although the practical task is quite simple, about 20 professional words are included, so at first glance the text is difficult, but the structure is quite simple and based on instructions / imperative
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
This task can with advantage be part of a "task based" process where text, video, and the tasks act as a pre-task followed by pair work where the students alternately instruct one other to assemble a plug.
The tasks for text and video are done with https://learningapps.org/ and pasted into Clilstore by selecting "paste / correct media" and then insert / "embed" the code with "embed" see below:
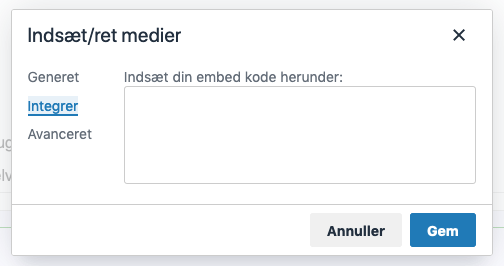
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The linguistic part of the assignment is based on giving and receiving instruction (imperative / bid form) and is quite simple. There are about 20 professional glosses (for example, wire cutter, fuses, strap), these are new to many students regardless of their origin.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after decoding the content in text and video proposes an analysis of the risks of working on live installations, which primarily involves lower order thinking LOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
1. Understanding the content of the text and being able to reproduce it.
2. To be able to transfer the situation, to actively wire a plug according to one instruction and then to instruct another to install a plug.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
There are important electrical engineering skills built into this unit, on the surface it is a simple exercise, but the vast majority of people will during the course of life be installing connectors (and extension joints) - and it is important to do this correctly, so that the wires cannot be pulled out and there are no possible short circuits when using the plug.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
Many people will buy extension cords in a supermarket, but in most cases they are too long and need to be shortened, doing this in a proper way is a necessary skill for everyone in the community. Many fires are caused by poor installations and plugs where the wires are not properly attached and at risk of short circuits between the conductors are part of these statistics.
 A terrible example of a wired plug, which can set the house on fire A terrible example of a wired plug, which can set the house on fire
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8201
Experiments with sinking and floating
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, we will work with nature and technology with experiments about sinking or floating objects. Students will learn through experiments what materials are flowing and which ones are sinking.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Throughout the experiment, students will learn about the materials that flow and which ones sink. They must guess and subsequently test whether they have guessed correctly.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
Students will learn new concepts about materials and gain a better understanding of the concepts of floating and sinking.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
Students should be able to draw conclusions about which materials can float and which ones sink and find the rules for this.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students become better at being able to conduct experiments based on a short description and can explain the concepts flow and sink. They learn to draw conclusions from their observations in the experiments and make generalizations.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
We work with this topic to give students a better understanding of the materials that surround them and learn about their characteristics in relation to water. It is important that students have an understanding of which materials are good for building things that need to float on water.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8227
Programming a traffic light
Learner level
A2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students work with programming. They must use their understanding of traffic lights to simulate its function. There are exercises where they train to read whether the LEDs are on or off.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Students become better at programming and learn to recognize whether they have turned on or off the pins. They learn how to connect the LEDs in the circuit to the microbi to make it possible for the students to control them using the programming.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
Students learn concepts related to programming and working with Microbits. They should be able to explain to others how their traffic lights work and how they have programmed it.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
In this course, students must use their knowledge of how a traffic light works and use it in their own programming. They should be able to plan the various steps in programming and keep track of which LEDs to light when..
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students should be able to explain how their programs are built and how they work. Students should be able to connect the LEDs to the microbite and know the concepts of cathode and anode.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
Students will gain a better understanding of how urban planning works and what is required by considerations to create a traffic light that can effectively control traffic.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8444
Calculation stories
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, the students learn to recognize mathematics in different stories from everyday life and they have to invent calculation stories themselves.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The students have to work with small situations from everyday life and find the math in them. They need to use their knowledge of addition and subtraction when compiling their own calculation stories.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The students must show that they have understood addition and subtraction by inventing calculation stories that make sense - both in relation to the story itself but also in relation to addition and subtraction.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The students must show through stories that they have understood addition and subtraction. In the stories, they must provide relevant information and ask a question that can be answered based on the story.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students can build stories that make sense in relation to the question.
Students can recognize the math in their everyday lives.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
Students can recognize situations from their everyday lives where maths can help them with a solution.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8445
The Tale of the Three Billy Goats Gruff
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
Students will study the fairy tale about Three Billy Goats Gruff where they will have to look for the characteristics of fairy tale. They have to use the classic adventure characteristics and the “contract model” to analyze the fairy tale. Finally, they are going to write their own fairy tale based on their knowledge of fairy tales.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Students are going to work on the fairy tale genre based on the fairy tale Three Billy Goats Gruff. They are presented with the characteristics of fairy tale and the “contract model”. They will use them to analyze the fairy tale.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
In pairs, students are going to analyze the adventure using the characteristics of fairy tale. They must know the fairy tale so well that they can reproduce it as a cartoon. The students will have to talk together when they are writing their joint fairy tale.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The students must be able to talk about the characteristics of fairy tale.
Students should be able to use the “contract model” to analyze the fairy tale.
Students become better at recognizing fairy tales when they hear one.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students get better at recognizing the classic characteristics of fairy tales.
The students learn how to use the” contract model” on a known fairy tale.
The students write their own fairy tale using the known characteristics of the genre.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
Fairy tales are an important part of our culture. Students must therefore know the fairy tale genre as well as what characterizes this genre.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8498
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Save the Egg: Trial and Error
Learner level
The Clilstore unit is made for teachers explaining how to implement teaching both science and language. The unit is suitable for teacher preparation as wel as for teacher training. The level of the teacher instructions is C1
N.B. there is a link from the Danish unit to lesson plans, handouts etc. in both Danish and English
The scenario is suitable for learners at levels A1-A2, but it can be used for all levels
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In "Trial and error" children from language level A1 and upwards can learn about the scientific method of trial and error, - to make a hypothesis, and to fill out a simple report on their experiments.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The students learn the mindset of the trial and error method.
They will have to:
•Think of a way to solve the problem they are facing
•Carry out their solution within the experiment
•Evaluate the outcome
•Rethink the first solution and make further developments based on the outcome
-Try again
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The students will, according to their language level:
-Communicate within their groups about how to solve the challenge of rescuing the egg from its brutal fate
-Show their approach in drawing and writing
-Use checking and confirmation strategies in order to enhance their vocabulary. How do you say…. ?
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
In the process of working with the Trial and Error method the students will move along the arrow of Blooms Taxonomy of Learning Behaviours.
In their attempts to understand the task they will move from the lower order thinking skills (LOTS) of remembrance and understanding to applying their findings to their analysis of how to solve the problem.In order to succeed, they will needto evaluate their approach and create asolution, ending up in the area of the higher order learning skills (HOTS).
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The students will:
- Understand an instruction and think through an experiment
- Set up a hypothesisUnderstand the method of trial and error and be able to use it
- Use language chunks to communicate about the experiment
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
The students will be able to see how:
- Facing challenges is part of today’s world and involves an experimental and problem-solving mindset, which is a very important skill in the ever-changing world of today
- Teamwork is important in today’s world, and the collective knowledge of each of the team individuals is a key competence for success
- Thinking laterally and using known materials in a new way and context motivates the students to be experimental and active in their own learning process and makes them realize potential problems and solutions in their everyday life
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8542
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
The Body / Kroppen N/T
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
This unit is about the human body and the organs.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The student has to see the video and afterwards answer questions related to the topic.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The student shows that he/she understands the topic by filling out a questionnaire and solving the tasks.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The student must show through the answer that he/she has understood what the body organs can do and why they are important for humans.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The student can answer the questions so it makes sense in relation to the knowledge he/she has acquired in the video. The student understands the importance of body functions, and has knowledge of how the organs work.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
The student can recognize situations where it may be good to know the body and the functioning of the organs.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8285
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Fractions / Brøker
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit the student learns about addition of fractions.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The student should start by watching an intro video about fractions, and then a video about how two fractions are added together. Finally, the student must try to solve some tasks based on the knowledge the student has acquired in the videos.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The student must show he/she has understood how two fractions are added together by solving the attached assignment.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
Through answering the assignment, the student must show that he / she has understood how two fractions are added together.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The student can solve the task, and possibly watch the video again if there is any doubt about how to solve the task.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
The student is able to recognize situations from everyday life where it can be useful to put fractions together.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8286
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
The Game Wheel / Spilhjulet
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students must work with the game wheel. They need to take a well-known ball game (e.g., pinball) and make it their own game.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The students should use the video to get an idea of how the game wheel works and how they can change a known game into their own version of the game.
Once they have changed the game, they have to test it on their classmates and see how it works.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The student must show that they understand how the game wheel works when they show the finished game to their classmates.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The students must, through the rules of their game, demonstrate that they understand what the game wheel is all about and how to use it in all kinds of ball games.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The students have to make some rules for their games that make sense and make the game fun.
They have to be good at listening to the feedback that are given, for example if they have to adjust some of the rules to make the game better.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
Students can recognize the ball game from their everyday lives, and have to think a little out of the box to make it their own game.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8287
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Handleplan mod børn og unges rygning
Learner level
B1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
Every day, 40 children and adolescents start smoking. The number is on the rise and almost every third of young people between 11 and 17 are expected to die from smoking if they continue to smoke as adults. Smoking is the single biggest cause of illness and death in Denmark and the biggest threat to public health.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Video and text from the Ministry of Health and the Elderly (December 18, 2019) on action plan against children and young people's smoking.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The first part of the assignment is to decode (listen and understand) the speech of the Health and Senior Minister and the text of the agreement, this can be followed by group work where the participants work group-wise with:
- What positive things do some young people start smoking?
- What is difficult when you want to quit smoking?
- Can you find more measures that could prevent smoking?
- There is virtually no one over the age of 30 who starts smoking, why?
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after the work of decoding the speech and subsequent text adds up to an analysis of the causes of young people's smoking, which involves both lower and higher order thinking LOTS and HOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
1. Understanding the speech content and being able to reproduce it (LOTS)
2. Being able to decode causes of smoking to critically relate to solutions (HOTS)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Participants are able to understand some of the causes of smoking, and especially to see how some are motivated to start smoking.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
In Denmark, 40 children and young people start smoking every day. The number is on the rise and almost every third of young people between 11 and 17 are expected to die from smoking if they continue to smoke as adults. Smoking is the single biggest cause of illness and death in Denmark and the biggest threat to public health.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8557
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
4More Productions (a business case)
Learner level
B1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
This case is based on a video recorded in 2005, in 2013 video and text were used for a task made in the first version of Clilstore. This new version shows new opportunities in Clilstore, including embedding a crossword puzzle done in Learningapps.org (web3 interaction).
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Three young media students talk about their collaboration on a start-up company. They have created a presentation video which includes examples of their products.
Video and text are utilized for a case where students must prepare a business plan based on the company 4More Productions.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The first part of the task is to decode (listen and understand) the case text and video, which can be followed by group work where the participants work with:
- Concepts from business theory
- Prepare a business case / business plan
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after the work of decoding video and text proposes an analysis of the 4More Production company's possibilities to establish itself in the market, which involves both lower and higher order thinking LOTS and HOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
1. Understanding the Case Content and Concepts of Business Doctrine (LOTS)
2. Being able to understand the market to which the service of the company is addressing and developing a realistic plan for developing the company (HOTS)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Participants will be able to develop a business plan based on the ideas behind the company, market analysis and customer base, budgets and marketing as well as preparation of a SWOT analysis.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
In modern society, there is a growing need for combined media and ICT skills, but in order for young people to be successful in creating a media business, it requires a thorough understanding of the concepts of business teaching and being able to see opportunities and limitations for a company by developing a company level.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/904
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Forstå den nye ferielov
Learner level
B1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
Video and text about the new Holiday Act, which comes into force on September 9, 2020. The Holiday Act entails major changes, which will ensure that new people in the labor market can obtain the right to paid vacation days.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Video and text explaining the new holiday law. After decoding the content of the law, there are assignments for group work that will ensure that participants understand the consequences of the law and can assess whether it has disadvantages for some people in the labour market.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The first part of the task is to decode (listen and understand) the content of the text about the agreement, this can be followed by group work where the participants work group-wide with
- What are the benefits of the law to new people in the labor market?
- Is the new vacation law a benefit for all employees?
Participants can search the web for the pros and cons of the new holiday law and then submit answers and arguments to the entire team.
The group work will facilitate practice in verbal communication.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The task after decoding the content of the video and subsequent text proposes an analysis of the meaning of the law, which involves both lower and higher order thinking LOTS and HOTS.
There are two objectives with the task:
- 1. Understanding the speech content and being able to reproduce it (LOTS)
- 2. Being able to assess the consequences of the law (HOTS)
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Participants gain an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of the Holiday Act and receive language training in being able to present the advantages and disadvantages of a law relating to the labor market.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
The new holiday law is rather comprehensive and can be difficult to understand. The government's communications department has compiled a video showing some of the differences between the old holiday law and the new one, which leads to faster earning of holidays for new people in the labour market.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8595
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Waste
Learner level
A2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students are working with waste and learning how to sort it.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
There is focus on different types of waste that students must relate to and learn to sort. We also learn about the arrangement for a deposit on packaging on bottles.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
Students must learn different concepts within the topic of waste and be able to explain to others about how they sort waste.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
In this topic, they must be able to relate to what is waste and what is recycling as well as how to sort different types of waste. They also learn about what happens to the things that can be recycled.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students become aware of how to sort the waste so we can recycle as much as possible.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
In our community, we all need to take responsibility so that we do not waste the resources that are in our waste. The students are therefore taught to recognize different types of waste and through the new knowledge become better to sort their waste themselves.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8787
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Spiders
Learner level
B1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit students learn about spiders.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
Students learn about the characteristics of a spider so they can tell the difference between insects and spiders. They learn about the hunting technique of various spiders as well as how to eat their prey.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
Students must learn the concepts that belong to spiders so that they can describe a spider themselves.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
Students learn about what a spider is and how it catches its prey.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
Students can explain to others what a spider looks like and how to tell the difference between a male and a female.
Students can explain how spiders catch their prey.
Students can find spiders themselves and use their knowledge to treat them respectfully.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
There are many people who are afraid of spiders without knowing what kind of animal it is. It is therefore important that students learn about spiders so that they learn to be curious about a topic that others find strange and learn to take a stand on them themselves.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8789
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Bearnaise sauce
Learner level
A1
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students will learn how to make their own béarnaise sauce from scratch
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The students will learn how to make their own béarnaise sauce by following a recipe and a video.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The students must learn the professional concepts that belong to the subject and learn the basic methods of making a sauce.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The students learn how to make a béarnaise sauce and where the tricky parts are.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The students can explain how to make a béarnaise sauce and how to avoid a spoiled sauce.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
It is a difficult task to make béarnaise sauce, so you need to have a bit of experience in the kitchen. Students must have an understanding of how important it is to follow the recipe and keep a close eye on the sauce throughout the process. In addition, students should be able to look at the process and find out where it went wrong if they did not have a finished sauce.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8825
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Coordinate system
Learner level
A2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students learn about coordinate systems and how they can use it in geogebra.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The student must learn how to use a coordinate system by watching the video and doing the assignments.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
The student must acquire knowledge so that they understand the different concepts within the subject coordinate system.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The student must understand how to use the coordinate system to plot points, make figures etc.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The student must be able to explain how they can use a coordinate system and in which contexts it is beneficial to use it.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
In our everyday life, a coordinate system can be used for many things, such as. to find the way or how far it is from point A to point B. Therefore, it is important that students get a knowledge of the coordinate system so that they know how it is used when they encounter it.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8826
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Angles
Learner level
A2
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Description
In this unit, students must work with angles. They have to go out and find angles in their immediate area.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Content
The student must learn how to use a protractor, and get to know the difference between the different angles.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Communication
By watching the video and doing the exercises, the student must learn about angles. They need to get to know the different concepts.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Cognition
The student must learn to understand how to measure an angle and how to make an angle.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Competences
The student must be able to explain what an angle is, how a protractor is used and what types of angles exist.
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
Community
In our everyday lives, there are angles everywhere, we often have to use them when we have to build things, for example. It may therefore be essential for the student to understand when the different angles are used and how they are used.
Go to the unit: https://clilstore.eu/cs/8727
 Back
to Top Back
to Top
|

The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents which reflects the views only of the authors, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.. |
|
|
|
|